Proxies and VPNs both enhance online security and privacy but serve different purposes. By understanding how these tools work, you can be in a strong position to protect your online activities.
Comparing proxy vs VPN, proxies act as intermediaries to bypass censorship and access restricted content, while VPNs create a secure, encrypted tunnel that safeguards all of your internet traffic. In this article, we will explore the key differences between proxies and VPNs, and guide you to choose the right solution for your needs. Let’s start by understanding what exactly a proxy is.
What Is a Proxy?
When you are accessing a website through a proxy, your request is going through a proxy server. The proxy server acts as an intermediary between you and your target website. Proxy server helps you access any geo-restricted content and bypass the censorship.
Let’s understand this in detail with an example. Let’s say you want to access a website named blockedwebsite.com which is blocked by your ISP. Note that whether you use a proxy or not, the request will first go to your ISP. However, when you are using a proxy, your ISP will not know that you want to access blockedwebsite.com. To the ISP, you are just accessing the proxy website URL and not the blockedwebsite.com. The ISP can block the proxy itself, however, It cannot check the final destination URL inside your request.
A proxy may or may not encrypt your data. However, it is still effective as an intermediary to access the censored content. Proxy can also mask your IP address and your location when your request reaches the final destination i.e. blocked website. There are many types of proxy servers, some are paid, and some are free. Some are more secure than others and so on. Proxy is a lightweight and simple solution to access censored content as you do not need to install any software. Proxies are usually faster, especially if you are connecting to a proxy server closer to your location.
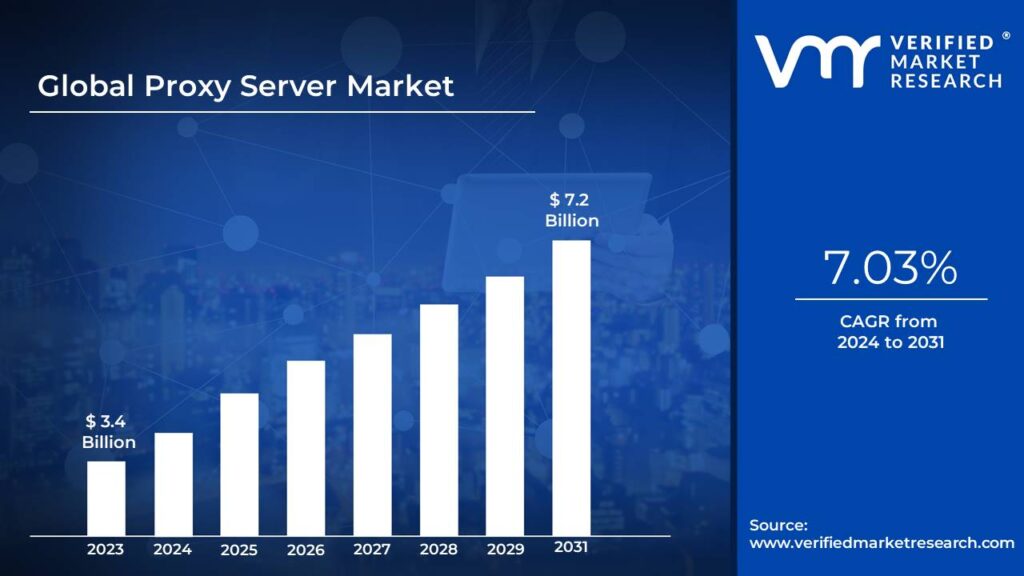
Proxies have a major role when it comes to anonymization. According to this report, the global proxy server market was valued at approximately $3.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $7.2 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.9%.
What Is a VPN?
VPN is another option if you want to access censored content. Just like a proxy, a VPN also acts as an intermediary between your device (laptop) and your target website. However, the differentiating factor is the encryption. A VPN creates a secure tunnel between your device and the VPN server and all the traffic is encrypted.
That means, no third party, not even your ISP can know what is being communicated between you and the VPN server. That makes VPN a highly secure solution especially when using public WIFI or sending sensitive information. VPNs are so important in today’s cybersecurity landscape that the global VPN market is projected to reach $75.59 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.2% from 2020 to 2027.
VPN solution generally requires you to install VPN client software that communicates with the VPN server. Like a proxy, a VPN also hides your actual IP address and location so your anonymity is maintained.
Now that we understand how a VPN and a proxy work, let’s go through the key differences between them.
Proxy vs VPN: Key Differences
Here are some of the core differences between VPN and proxy.
- Data Encryption:
Proxy: May or may not encrypt your data, depending on the type of proxy used.
VPN: Encrypts all your internet traffic, ensuring secure and private browsing. - Anonymity:
Proxy: Masks your IP address when accessing websites but does not provide full anonymity since data is not fully encrypted.
VPN: Completely hides your IP and encrypts your data, offering higher levels of anonymity and privacy. - Traffic Coverage:
Proxy: Usually works on a specific app or browser level, so only traffic from that application is routed through the proxy.
VPN: Encrypts all internet traffic on your entire device, regardless of the application or browser. - Security:
Proxy: Provides basic security; however, without encryption, it leaves your data vulnerable.
VPN: Provides strong security by encrypting all data and protecting against potential cyber threats. - Software Requirement:
Proxy: Typically does not require software installation; you just configure it in your browser or app.
VPN: Requires installing VPN software or an app to set up and maintain an encrypted connection. - Speed:
Proxy: Usually faster because it doesn’t encrypt traffic, but it depends on the distance to the proxy server.
VPN: Slightly slower due to the encryption process, although modern VPNs minimize this difference. - Bypassing Geo-restrictions:
Proxy: Can bypass some geo-blocks, but not as reliably as a VPN.
VPN: More effective in bypassing geo-restrictions, especially for services like streaming or censored content. - Cost:
Proxy: Often free or low-cost, but premium options with added features are available.
VPN: Typically requires a paid subscription, especially for premium, high-security VPN services.
Below diagram (source) elaborates on the difference between a proxy server and a VPN.
When to Use a Proxy
Proxy is a good option if:
- You want to access the geo-restricted or blocked content without needing encryption.
- You want to hide your IP address for basic anonymity.
- You want to bypass any network restrictions imposed by your office or school network.
- You have web scraping needs and want to rotate your IP address during the automatic data collection process to avoid getting blocked.
When to Use a VPN
VPN is a good choice if:
- You are using public wifi (e.g. airport, cafe) and want to encrypt your internet communication so that it is protected from hackers.
- If your country has strict internet censorship on the government level and you want to access restricted websites
- You are working from a remote location and want to connect to your office network securely
- You have a need for full anonymity so that you are not tracked by your ISP or advertisers.
- You want to anonymize torrenting activities and avoid ISP throttling or legal issues when downloading copyrighted content
Proxy vs VPN for Specific Tasks
While the functionality of both proxy and VPN overlap to some extent, there are certain tasks for which you would prefer VPN over proxy or vice versa. Below we have compiled a list of tasks that are suitable for each of these solutions. While this might not be a complete list, it still covers most of the common scenarios.
Tasks where proxy should be used
- Automating data collection from websites for research or business intelligence. E.g. data mining and web scraping
- Accessing social media or streaming sites blocked on your institution’s network.
- Testing website performance from different Regions, e.g. as a web developer, you need to see how your site loads in various countries.
- Reading an article or accessing a service not available in your country.
- Reducing bandwidth costs with caching proxies. E.g. You want to use cached content in a corporate network where multiple users access the same resources.
- You want to hide your IP address while casually browsing the internet
- Load balancing in high-traffic scenarios, e.g. you want to distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use and prevent overload.
- Bypassing simple IP bans e.g. You want to regain access to a forum or service where your IP has been banned.
- Using a public or shared computer where you can’t install software. Proxy can be easily configured in a web browser.
Tasks where VPN should be used
- Securing data on public wifi. E.g. you are at a coffee shop or airport using public Wi-Fi to check your emails or bank account.
- You are working from home or traveling and need to access your company’s internal network and resources.
- You want to download or upload files via torrent networks.
- You live in or are visiting a country with strict internet censorship and want to access blocked websites like social media or news outlets.
- Protecting VoIP e.g. You want to make voice or video calls over the internet using services like Skype or WhatsApp.
- Securing online banking and financial transactions e.g. You want to perform online transactions involving credit cards or bank accounts.
- You are abroad and want to access services (e.g., banking, streaming) that are only available in your home country.
There will be, however, some scenarios where you would prefer to combine both a proxy and a VPN. Let’s go through those scenarios as well.
Proxy and VPN Combined
Both the proxy and VPN have their own use cases that we discussed above. However, there are certain situations where you might have to combine both of these options not just for anonymity but for full encryption of your communication as well. Here are some of those scenarios:
- Use a VPN for full data encryption and a proxy to route specific traffic (e.g., media streaming or web scraping) through different locations to avoid being traced.
- A proxy can mask the use of high-bandwidth services (like streaming) from your ISP, while the VPN encrypts all traffic. This combination makes it harder for ISPs to throttle your connection.
- Use a proxy for rotating IPs in different locations while maintaining a VPN connection for secure, encrypted access to websites without exposing your real identity.
- You can connect to your company’s secure VPN to access local network resources while routing non-work-related traffic through a proxy to access geo-blocked websites.
- In highly restricted environments (e.g., countries with strict censorship), combining a VPN with a proxy can add an extra layer of obfuscation, helping bypass deep packet inspection (DPI) and firewalls.
Conclusion
Both proxies and VPNs help you improve online security, but they have different strengths. Proxies are fast and easy, ideal for bypassing restrictions without encryption. On the other hand, VPNs provide complete security by encrypting your data, making them a better choice for sensitive tasks. Understanding your needs will help you decide whether a proxy or VPN is the best solution for your online safety.